What Does Cyber Insurance Cover?
Table of Contents
- By Rita
- Published: Apr 08, 2022
- Last Updated: May 24, 2022

There are numerous types of cyber-attacks, and they are an increasingly significant problem for all organizations. Many of these companies obtain cyber risk insurance to protect against some of the impacts of an incident. Companies and employees need to understand what cyber insurance is, who needs it, and what it covers.
What Is Cyber Liability Insurance?
Cyber insurance, also known as cyber liability insurance or cyber risk insurance, is designed to protect organizations from cyber threats in the digital age, such as data breaches or malicious cyber hacks.
A policy can help reduce damages in a cyber incident and its mitigate the aftereffects. Existing cyber liability insurance policies may provide coverage for cyber risks. For example, some commercial property policies may help with cyber threats.
Despite this, more and more businesses are taking up more specialized cyber risk insurance policies to complement their existing insurance arrangements, especially if they:
- Rely heavily on IT systems and websites for business operations.
- Possess sensitive customer details like names, addresses, social security numbers, and banking details.
- Process payment card information.
However, cyber risk insurance doesn’t kick in for everything. An organization must understand what is and isn’t covered when it signs up for a policy. For example, breaches caused by outsourced services aren’t usually covered unless specified. So, a deep understanding of your business’ risk areas is vital before choosing a plan.
Even with cyber liability insurance, a business is still responsible for setting up preventative measures and creating a robust cyber security plan. Cyber insurance coverage isn’t a substitute for regular security updates and employee education.
Who Needs Cyber Insurance Coverage?
Every business needs cyber insurance, as almost every organization relies on technology to operate. Any business that operates online or is dealing with electronic data may will benefit from cyber risk insurance.
Businesses that deal with large amounts of private personal data could also benefit significantly from cyber liability insurance. This information could include personal data of customers and employees, intellectual property, or financial data, all of which are potentially profitable to cybercriminals.
Hackers can also impair a network with ransomware. Having a cyber risk insurance policy covering ransomware could help organizations plagued with such attacks find a way out of the predicament.
While we recommend cyber insurance coverage to all businesses, some may benefit more than others. Organizations with the following risk factors should immediately find a policy or consider raising their coverage.
Small and Medium-Sized Businesses
Most cyber criminals don’t have the resources or guts to go after the big guy. While attacks on industry giants like Target and Equifax make the biggest headlines, smaller businesses are at roughly three times the risk of attack.
Additionally, more modest businesses tend to invest less in cyber security measures or can’t afford to update their strategy constantly. These firms can plan their cyber insurance policies to shore up their weaknesses.
Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers, especially smaller practices, absolutely require cyber insurance coverage. These operations handle and store sensitive patient information like billing details, social security numbers, contact information, physical attributes, prescriptions, and pre-existing conditions.
Stealing this information allows scammers to craft more believable social engineering attacks, making clinics a prime target. Additionally, if a healthcare provider’s business identity is stolen, their name could be used to scam others.
Financial Institutions
Banks and credit lenders are also at increased cyber risk due to the large amounts of financial and personal information they keep. Collected data includes credit card details, routing information, social security numbers, and account PINs.
Financial services are one of the most strongly secured industries, but there are always new vulnerabilities for criminals to attack.
Utility Companies
This inclusion may seem out of place. However, utility providers are vital to society and accounted for over 15 percent of known attacks in 2020. Shutting down electricity, water, gas, or the internet causes substantial disruption to people’s lives. Consumers become impatient and are quick to lose trust in your services.
So, energy companies are much more desperate to continue operations. This gives them less time to respond to ransomware threats and cave to criminal demands. It doesn’t help that utility companies are known for having dated security systems in place.
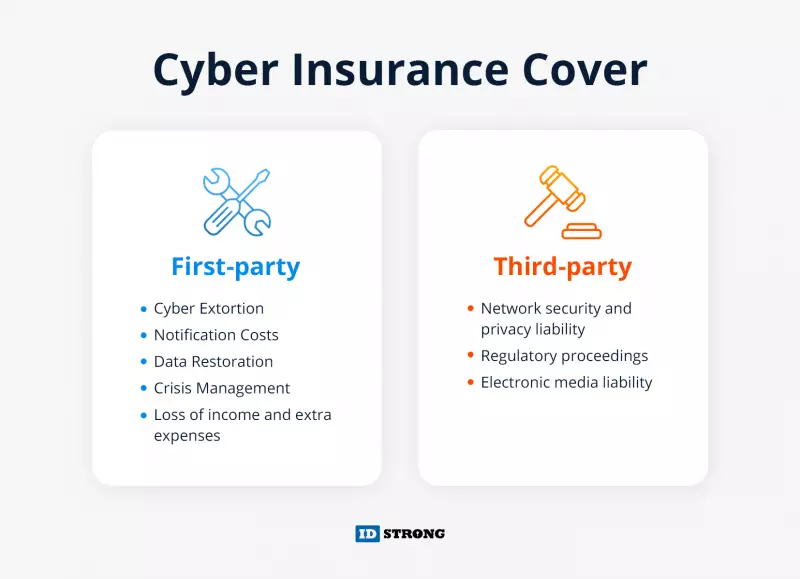
What Does Cyber Liability Insurance Cover?
Generally, cyber risk insurance covers the losses arising from damage to or loss of information from IT systems and networks.
Usually, cyber risks are categorized as first party and third-party risks. Insurance products exist to cover these types of risks.
First-Party Insurance
First-party coverage pays out-of-pocket expenses that a firm directly incurs because of a breach or covered event.
Cyber Extortion
This covers ransoms paid to cybercriminals who’ve breached a company’s computer system. Ransomware threatens to commit a despicable act like destroying data, infecting systems with viruses, conducting an attack, or revealing private information unless an exorbitant amount is paid.
Another form of cyber extortion includes Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks which overwhelm networks with information until they shut down. Legitimate users are denied access, and business grinds to a halt.
These policies usually cover extortion payments made to the cybercriminals with the insurer’s consent and other related expenses like hiring an expert negotiator.
Notification Costs
These policies cover the cost of notifying customers whose data has been affected by the breach. The labor hours associated with compiling a list of victims and mailing letters come at a substantial cost.
All US states and territories have consumer laws that require businesses to inform individuals when their personally identifiable data is compromised. If the breach is large enough, they are also forced to give a public explanation.
How far businesses have to go to inform consumers of a breach depends on many factors. Details like the severity of the breach and the company’s industry play a large role. You may be liable for setting up a call center to provide credit monitoring services, and these policies may cover the cost of that.
Data Restoration
Data restoration encompasses any costs related to restoring data or any software that may have been compromised during a hacking incident. The first step is to isolate affected systems to prevent further theft. This is why creating a segmented network is so important.
After retrieving data from backups or specialized software, businesses must take time off to verify the integrity of the restored files. This process can span weeks or months, depending on how detailed it is and how many third parties must confirm.
Crisis Management and Public Relations Expenses
The cost of hiring experts in the field may be covered. These would all be potentially helpful in determining the extent of the damage, finding what information was compromised, helping reduce the loss, and aiding in any reputational damage.
Crisis management firms assist by creating press releases that soften public backlash and recount events in a more positive light. The negative response to Target’s data breach caused estimated losses of up to $1 billion due to shopper’s waning trust in the retailer.
Loss of Income and Extra Expenses
Covers any income losses that a business sustains and any additional costs it incurs to restore operations after a shutdown caused by a hacker attack, virus, or other covered online danger. This is also known as business interruption coverage.
For example, if an electric provider is shut down due to an attack, business interruption coverage can repay the company what it would have earned from energy used in those hours. Also, if the company needed to hire temporary technicians to check power lines and meters, the policy could cover that cost.
Fraud Coverage
Fraud coverage is generally categorized under crime insurance, but it still applies to financial losses from cyberattacks. Some policies focus on payment card fraud which reduces the impact of selling products to people using stolen credit card information.
Other cyber insurance coverage covers social engineering fraud in which scammers trick employees into transferring company money or leaking sensitive information. This applies even in cases of employee theft where the employee willingly leaks the information.
This type of coverage is useful for “whale phishing” cases where management executives with more power are targeted and there’s been significant damage.
Third-Party Insurance
Third-party coverage applies to damages or settlements a business should pay due to claims or suits arising from the business’ actions or failure to act. It may include:
- Network security and privacy liability - Covers claims against the business resulting from negligent acts, errors, or omissions. It includes failure to protect sensitive information, failure to notify of a data breach, and failure to prevent a security breach that leads to a DoS attack or introduction of a virus.
- Regulatory proceedings - Covers fines or penalties levied on the business by regulatory agencies that regulate data breach laws. It also helps cover the cost of hiring a lawyer to respond to a regulatory proceeding.
- Electronic media liability - This insurance covers lawsuits against the business for libel, slander, defamation, copyright infringement, or privacy invasion.
What Isn’t Covered by Cyber Insurance?
As is the case with any insurance policy, there are exclusions in cyber policies that potential policyholders should note. Some of the things that a cyber risk policy might not cover are losses caused by the following:
- Known and unaddressed vulnerabilities – If you've ignored a weakness, then insurers may consider an attack an "avoidable risk" the company had a responsibility to fix.
- Terrorism – Many terror attack cases aren't categorized under cyber security and may require separate insurance. This is more likely if a foreign power performs the attack.
- Intentional Fraud – You'll be hard-pressed to find an insurer that allows dishonest practices like fraud and embezzlement. Deliberate fraud may extend to a company's failure to follow through on promised cybersecurity initiatives.
Every insurer and policy is a little different. You must carefully review the terms to know what is covered and what's not. Nothing is worse than thinking you have a safety net only to fall much further than expected.
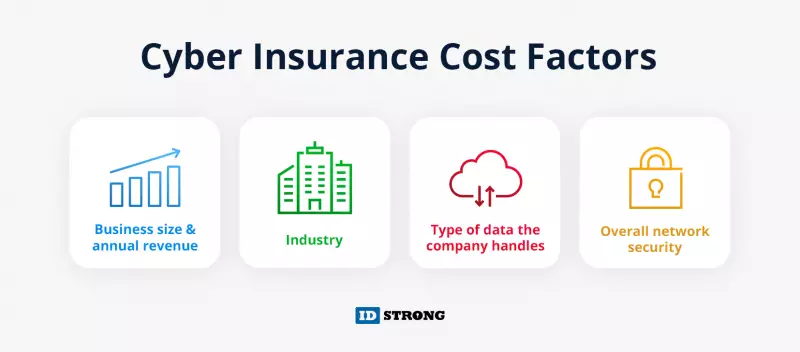
How Much Does Cyber Insurance Cost?
As with traditional insurance, cyber insurance providers look at the potential risks of covering each business. The cost of a cyber-risk policy usually depends on several factors:
- The size of the business and its annual revenue – The amount of data a business collects is tied to its customer pool. The more information a company loses, the more likely it’ll face additional disciplinary action and costs. Larger organizations face higher premiums.
- The industry the company operates in – Certain sectors, such as healthcare and finance, are at higher risk of attack. They also face more sophisticated threats, which increases the possibility of requiring a high payout.
- The type of data the company usually deals with – There are heftier fines for losing people’s social security numbers compared to losing names and primary contact information. Insurance providers consider this and jack up premiums accordingly.
- The overall security of the network - A business with poor cyber security systems or a previous history of falling victim to data breaches would be charged more for an insurance policy than one with a good reputation for upholding security standards.
Small businesses can get away with paying a few thousand yearly, but larger enterprises should budget tens or even hundreds of thousands of dollars to protect themselves.
What Do I Need To Apply for a Cyber Liability Insurance Policy?
Cyber risk insurance isn’t a foolproof solution for all your cyber security problems. Your business may have to prove that it takes its cyber security seriously to get the best deal. Many insurers will not take on a customer that looks like they may be at great risk for a data breach.
Usually, when applying for a policy, insurers will ask to assess the cyber security your company has in place. You’ll be required to maintain accurate details about your cyber security as time goes on.
Policies are reassessed every 12 months. Even after getting a policy, you still need to maintain proper cyber security procedures or risk losing your insurance down the line.
You also have to understand the systems and data essential to your business and assess whether the level of coverage you get is adequate.
Deciding on the appropriate cyber liability insurance policy goes beyond the IT department. This is also a concern for upper executive management.
Unlike other incidents like fire or theft, cyber incidents are often spread out over the whole organization. You must have a great understanding of your organization’s operations and how departments intermingle to determine the extent of any incident.
It’s beneficial to invest in your business's cyber security, even if it has a cyber liability insurance policy.
What Is the Future of Cyber Liability Insurance?
The regularity of cyber-attacks is expected to remain a risk. Cybercriminals are also likely to become bolder with their schemes. As a result, the way cyber risk insurance operates will evolve.
Cyber insurers are unlikely to offer policies to organizations that pay little concern to their cyber security.
Paying out insurance policies is purely reactive and quite costly for insurance providers. Many insurers have now become focused on risk aversion. Not only do they offer payouts if a cyber attack should occur, but they are encouraging customers to take a proactive approach to cyber security.
The insurance industry evolved from a lender of last resort and payouts to a risk advisor and partner for your business operations
















